ZMPT101B AC Voltage Transformer Sensor Module
Updated: 21Aug2024 03:42:09 UTC 2024-08-21T03:42:09Z
Rating: (0 reviewsThis article has not been rated yet)
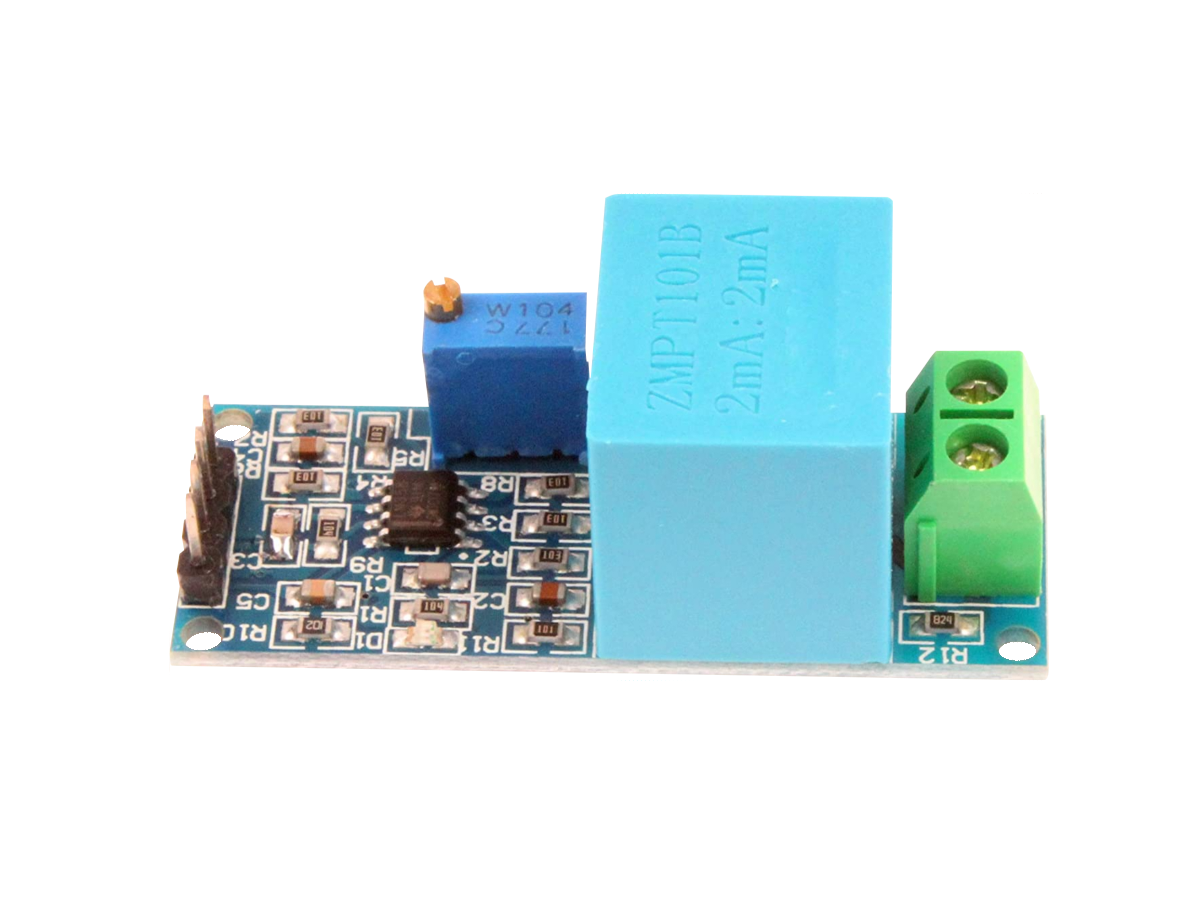
The ZMPT101B Single Phase AC Voltage Transformer Module can measure AC voltages up to ±250V (50Hz/60Hz) and outputs a scaled down AC voltage between 0V and VCC (5V - 30V) with a DC offset of VCC/2.
The ZMPT101B module comes with a multi turn trim potentiometer for adjusting the amplitude of the output waveform around the DC offset to make the output range suitable for an external ADCAnalog-to-Digital Converter (ADC, A/D, or A-to-D).
This hardware overview of the ZMPT101B AC Voltage Transformer Module covers specs, board layout, pinout, schematic, and calibration.
As a word of caution, when messing with mains electricity, power line, or wall outlet power, make sure you know what you are doing and be careful because it can kill you.
Specs
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Model | ZMPT101B Single Phase AC Voltage Transformer Module |
| Input |
|
| Output |
|
| Operating Voltage (VCC) | +5V to +30V DC | Board Size | 49.5mm x 19.4mm (1.95in x 0.76in) |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Model | ZMPT101B Transformer by InnovatorsGuru, Qingxian Zeming Langxi Electronic |
| Rated Input Current | 2mA |
| Rated Output Current | 2mA |
| Linear Range |
0 to 1000V
0 to 10mA |
Isolation Withstand Voltage | 4000V |
| Turns Ratio | 1000:1000 |
| Phase Angle Error | ≤ 20' (50Ω) |
| Measurement Accuracy Class | 0.2 |
| Linearity | 0.1% |
| Rated Burden | ≤ 200Ω |
| Dielectric Level | 3000VAC/min |
| Frequency Range | 50Hz to 60Hz |
| DC coil Resistance | 110Ω at 20°C |
| Operating Temperature | +40°C to +70°C | Size (LxWxH) | 19.5mm x 17.0mm x 19.0mm 0.77in x 0.69in x 0.75in |
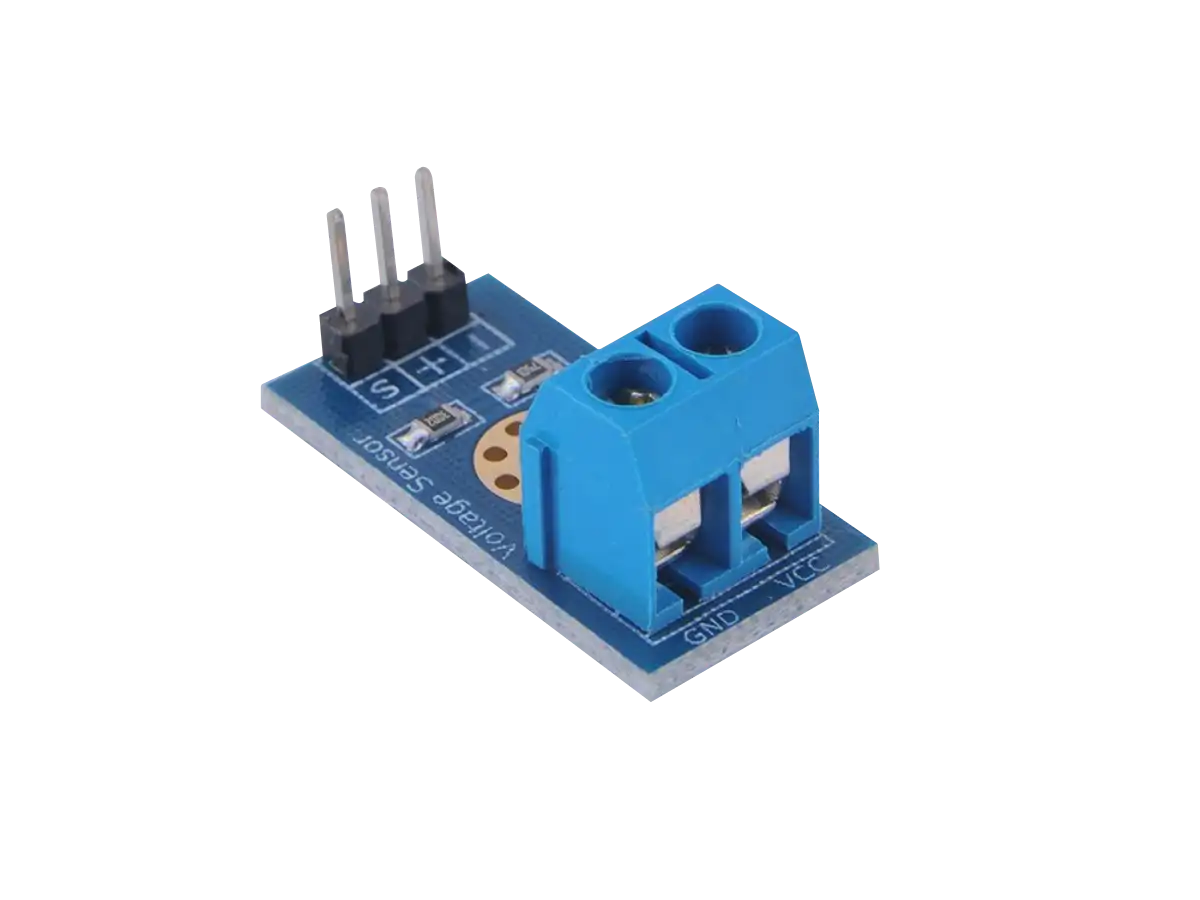
Board Layout
The board layout for the ZMPT101B module is shown below. The board features an LED power indicator when 5V to 30V DC is applied to the VCC and GND pins. The Single Phase AC Hot Line (L) and Neutral (N) are inputs into the module to the ZMPT101B transformer that isolates the circuit and significantly reduces the voltage.
The output of the transformer is amplified by LM358 dual OpAmp chip to produce an analog voltage on the OUT pin in the range of 0V to VCC appropriate for an external ADC, where the multi turn trim potentiometer can make the amplitude smaller is needed.
| Pin | Function |
|---|---|
| Line (L) | Input hot AC line L is a current carrying conductor within ±250V RMS |
| Neutral (N) | The input N is the Neutral and returns current to where it originated - in a house that is the main circuit breaker panel or fuse box. |
| VCC | 5V to 30V DC to power the OpAmp IC, the power indicator LED, and the output. |
| OUT | Analog output in the range 0V to VCC with a DC offset of VCC/2. Adjusting the potentiometer changes the amplitude of the output waveform, but not the DC offset. |
| GND | Common ground for VCC power and output. This is not common to the input line (L) and neutral (N). |
The schematic for the ZMPT101B module is shown below. In the primary circuitry, the ZMPT101B transformer reduces the input AC voltage in the range of ±250V (50Hz/60Hz) down to Vout = Vin(R1/R2), where R1 is 100Ω and R2 is 820kΩ. When the input voltage is at its maximum of ±250V, the output of the transformer is about 30.5mV.
The secondary circuitry is a two-stage band-pass amplifier using an LM358 dual OpAmp IC. The LM358 has low power consumption and a wide operating voltage range of +5V to +30V DC from VCC. This amplifies the voltage in the range of 0V to VCC with a DC offset of VCC/2 for the OUT pin.
The amplitude of the output waveform is adjustable by the multiturn trim potentiometer, but does not change the DC offset.
Calibration
The output signal of the ZMPT101B module consists of analog voltages in the range of 0V to VCC and centered around VCC/2, with amplitude adjustable by the potentiometer. This means the analog output signal values needs to be calibrated to find the sensitivity scale factor so the output values can be scaled back to the original input voltages in the ±250V range. The sensitivity scale factor is the ratio of the input RMSRoot Mean Square voltage to the output RMS voltage (with the DC offset removed).
In order to calibrate you will need another voltmeter (preferably a True RMSRoot Mean Square meter for more accuracy) as a reference to determine the input RMS voltage.
To find the output RMS voltage you can record many samples from the ZMPT101B module with an ADC and take the RMS of the samples (averaging more samples will help eliminate noise as an error source in the sensitivity scale factor). The RMS is computed by first removing the DC offset from the output, then square the values, then take the average of the squared values, and finally take the square root of the average result.
The ZMPT101B module will output the DC offset when no input voltage detected, which should be about VCC/2, but different modules will vary slightly so this should be measured. Once the RMS of the ZMPT101B module is computed the sensitivity scale factor can be computed.
Once the sensitivity scale factor is obtained, the input voltages levels can be computed (either in firmware in a microcontroller or computer software) from the ADC measurements of the ZMPT101B module by just removing DC offset and scaling by the sensitivity.




(1) Comments
Sign in to leave a comment
Sign In
Most useful information for our project.