Raspberry Pi 4B Hardware Overview
Updated: 17Aug2024 09:03:39 UTC 2024-08-17T09:03:39Z
Rating: (0 reviewsThis article has not been rated yet)
The Raspberry Pi 4 Model B (RPi4B) is an SBCSingle Board Computer capable of dual HDMIHigh-Definition Multimedia Interface 4K4K resolution refers to a horizontal display resolution of approximately 4,000 pixels. In television and consumer media, 3840 x 2160 (4K UHD) is the dominant 4K standard. video display, USBUniversal Serial Bus peripherals, audio, video, 40-pin GPIOGeneral Purpose Input Output interface, Ethernet, and WiFi/BTBluetooth connectivity. It was launched by the Raspberry Pi Foundation in June of 2019.
This hardware overview of the RPi4B covers specs, board layout, pinout, processors, memory, I/O, and power.
This RPi4B consists of a quad-core 1.5 GHz 64-bit Broadcom 2711 Cortex-A72 ARMAdvanced Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) Machines processor and currently comes in three different variants of LPDDRLow-Power Double Data Rate4 SDRAMSynchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (2GB, 4GB, and 8 GB).
The board I/OInput/Output consists of a USBUniversal Serial Bus Type-C for power, 2x USBUniversal Serial Bus 3.0, Dual 4K4K resolution refers to a horizontal display resolution of approximately 4,000 pixels. In television and consumer media, 3840 x 2160 (4K UHD) is the dominant 4K standard. Micro HDMI Video, microSDThe microSD is a Secure Digital (SD) removable miniaturized flash memory card that is the compact version of a standard SD card and is meant to be used with smaller devices. UHSUltra High-Speed, Gigabit Ethernet, Bluetooth 5.0 BLEBluetooth Low Energy and Dual-Band 2.4GHz 802.11IEEE 802.11 is a set of protocol standards that define communication for a Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN). In order for WiFi to work between different devices, they all need to agree on how they are going to communicate. The current version of the standard is IEEE 802.11-2007, with many amendments such as 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, and 802.11n.N and 5GHz 802.11AC WiFi.
The board power needs a high quality true 2.5A power supply: it will consume around 1.5A of current by itself and secondary accessories can drive up current consumption to 2.5A. The official Raspberry Pi power supply (SC0218) is rated at 5.1V 3A.
Specs
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Info |
Raspberry Pi 4B
|
| Processors |
Broadcom BCM2711 SoCSystem On a Chip
|
| Memory |
|
| USB |
|
| Ethernet | 1x RJ45RJ45 is the most common type of the connector used for Ethernet networking. RJ stands for “Registered Jack” and 45 refers to the interface standard number. It has eight pins, which means that it contains eight separate wires. Gigabit Ethernet port |
| Wireless |
|
| Video & Sound |
|
| Multimedia |
|
| GPIOGeneral Purpose Input Output |
Standard 40-pin GPIOGeneral Purpose Input Output header (fully backwards compatible with previous boards)
There are no analog inputs on the RPi4B, since there is no onboard ADCAnalog-to-Digital Converter (ADC, A/D, or A-to-D), but you can connect an external ADCAnalog-to-Digital Converter (ADC, A/D, or A-to-D) module that communicates with the board by I2CInter-Integrated Circuit. Also referred to as IIC or I2C. or SPISerial Peripheral Interface. |
| Power |
Note: A good quality 2.5A power supply can be used if USB peripherals consume less than 500mA total. |
| Operating Temperature | 0°C to +50°C (+32°F to +122°F) |
| Board Size (LxWxH) | 85mm x 56mm x 19.5mm (3.35in x 2.21in x 0.77in) |
The RPi4B board is about the size of a credit card. The board dimensions (excluding the sockets) are 85mm (3.35in) in length and 56mm (2.21in) in width. Detailed dimensions for different parts of the board are shown in the figure below (source RPi4B Mechanical Drawing PDF).
RPi4B Board Layout
Processors
The RPi4B System On a Chip (SoCSystem On a Chip) is an ICIntegrated Circuit that has both a Central Processing Unit (CPUCentral Processing Unit) and a Graphics Processing Unit (GPUGraphics Processing Unit) integrated into the SoCSystem On a Chip, each with their own memory used as registers for their operation. The CPU performs operations such as basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, and I/OInput/Output, while the GPU is used for handling multimedia tasks such as video, digital image processing, drawing 3D graphics, and playing games.
The RPi4B SoCSystem On a Chip chip is a Broadcom BCM2711 that contains a 1.5GHz 64-bit quad-core Cortex-A72 ARMAdvanced Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) Machines v8 architecture core CPUCentral Processing Unit processor (Wikipedia ARM Cortex-A72) and a Broadcom VideoCore VI GPUGraphics Processing Unit processor (Wikipedia VideoCore).
There are three different versions of the RPi4 available: the RPi 4 Model B, the Compute Module 4, and the RPi 400 computer-in-a-keyboard. The SoCSystem On a Chip on the Model B is a Broadcom 2711ZPKFSB06B0T, while the SoCSystem On a Chip on the CM4 and RPi 400 are both 2711ZPKFSB06C0T (note the revision change from "B" to "C").
The BCM2711B0 contains the following peripherals that may be accessed by the ARMAdvanced Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) Machines.
- Timers:
- Allows software to be time-dependent for scheduling and synchronizing.
- Interrupt Controller:
- Allows the OSOperating System to handle all the computer resources, both internally to the SoCSystem On a Chip and externally (e.g., I/OInput/Output devices), and determine when the CPUCentral Processing Unit is ready for new instructions.
- GPIOGeneral Purpose Input Output:
- Enables control of connections, input, output, and different modes of the GPIO pins.
- USBUniversal Serial Bus:
- Controls the services and provides protocols for data I/OInput/Output, allowing peripherals to communicate with the RPi.
- PCMPulse-Code Modulation / I2SInter-IC Sound:
- PCM is a digital representation of an audio signal and converts digital sound data to analog signals needed for speakers and headphones. I2S is an electrical serial interface used to transmit PCM data from when connecting audio devices.
- DMADirect Memory Access Controller:
- Direct Memory Access that allows an I/OInput/Output device to bypass the CPUCentral Processing Unit and send/receive data directly to the main system memory for speed and efficiency.
- I2CInter-Integrated Circuit. Also referred to as IIC or I2C. Masters:
- Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) used for communicating with lower-speed peripheral devices like sensors and microcontrollers.
- SPISerial Peripheral Interface Masters:
- Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) used for communicating with higher-speed peripheral devices and allowing the daisy chaining of devices.
- UARTUniversal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitters:
- Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter (UART) used for serial communication between different devices.
- PWMPulse-Width Modulation:
- Pulse-Width Modulation used to generate pulses with a specified duty cycle to control the brightness of LEDLight Emitting Diodes, control motors, and can provide limited analog-like output.
More details on the interfaces and registers of these peripherals can be found in the BCM2711 ARM Peripherals Datasheet (PDF). The purpose of this datasheet is to provide documentation in enough detail to allow a developer to port an operating system to the BCM2711. The full datasheet and schematics for the 2711ZPKFSB06B0T chip is not available to the public because it is proprietary hardware. Broadcom only provides the datasheet under a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDANon-Disclosure Agreement).
CPU
The RPi4B SoCSystem On a Chip contains a 1.5GHz 64-bit Quad-Core Cortex-A72 ARMAdvanced Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) Machines v8 architecture core CPUCentral Processing Unit processor (Wikipedia ARM Cortex-A72). The specs for this CPU are given in the table below.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| ISAInstruction Set Architecture | ARMAdvanced Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) Machinesv8-A (64-bit) |
| Microarchitecture | Cortex-A72 |
| Release Date | Q2 2019 |
| Cores | 4 |
| Threads | 4 |
| Core Architecture | Normal |
| Frequency | 1.5GHz |
| Hyter-Threading? | No |
| Overclocking? | Yes |
| Turbo (1 Core) | No Turbo |
| Turbo (4 Core) | No Turbo |
| Lithography | 28nm |
| L1 Cache Memory |
32KB data + 48KB
instruction L1 cache per core |
| L2 Cache Memory | 1MB shared by all cores |
| Max Memory Bandwidth | 4.4GB/s |
| Max PCIePeripheral Component Interconnect Express Lanes | 4 |
| TDPThermal Design Power | 4W |
All computers have multiple levels of memory caching. The fastest data transfers to and from caches are the are the ones embedded in the CPU. They are called L1, L2, L3, etc. caches, which means Level 1, Level 2, Level 3, etc. The higher the level number, the larger the cache can be but at a cost of being slower.
The ARMAdvanced Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) Machines Cortex-A72 processor memory architecture has a two level cache structure: a Level 1 (L1) data cache and unified Level 2 cache. There is one L1 cache per core and all four cores share the L2 cache. Primary memory is the third and final level beyond L2 cache.
One advantage the RPi4B Cortex A72 has over its predecessors is a 15-instruction pipeline depth that provides out-of-order execution so it's not waiting for the output of one process to start on another. This makes it a lot faster than the RPi 3B+.
The BCM28711B0 also features a PCIePeripheral Component Interconnect Express link that connects the USBUniversal Serial Bus 2.0 and USBUniversal Serial Bus 3.0 ports, with the ability to access more memory than previous Pis and a separate Ethernet controller all leading to a greatly improved GPUGraphics Processing Unit feature set with much faster I/OInput/Output.
GPU
The GPUGraphics Processing Unit integrated into the BCM2711 SoCSystem On a Chip chip is a Broadcom VideoCore VI low power processor (Wikipedia). The specs for this GPU are given in the table below.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| GPU Integrated Graphics | Broadcom VideoCore VI (32-bit) |
| GPU Execution Units | 4 |
| GPU Shading Units | 64 |
| GPU Clock | 500MHz |
| GPU FP32 Floating Point |
13.5GFLOPSGiga (one billion) FLoating point Operations Per Second to 32GFLOPSGiga (one billion) FLoating point Operations Per Second
(estimates and calculations vary) |
| Max Display Resolution | 4Kp604K resolution refers to a horizontal display resolution of approximately 4,000 pixels. In television and consumer media, 3840 x 2160 (4K UHD) is the dominant 4K standard. The p stands for progressive scan, i.e. non-interlaced. The 60 stands for 60 frames per second. |
| Video Decoding |
|
| Video Encoding | H.264H.264 is a video compression standard also referred to Advanced Video Coding (AVC) or MPEG-4 Part 10 1080p301920 x 1080 progressively displayed pixels; also known as Full HD or FHD, and BT.709. 1,920 pixels are displayed across the screen horizontally and 1,080 pixels down the screen vertically. The p stands for progressive scan, i.e. non-interlaced. The 30 stands for 30 frames per second. |
As with any computer, on board graphics processors use RAMRandom Access Memory for graphics memory which is shared with the CPU. According to the RPi configuration documentation, the GPU memory settings in the configuration file (config.txt) sets the memory split between the CPU and GPU. Whatever value the GPU memory is set to, the CPU gets the remaining memory. The minimum value is 16MB, the default value is 64MB, and the technical maximum value is 944MB although values above 512MB will not provide increased performance and should not be used.
RPi4B V3DVirtual Three Dimensional has it's own MMUMemory Management Unit so textures and other GLGraphics Library resources are not allocated from GPU memory, but rather are allocated from Linux system memory. This means that gpu_mem can be set to a lower value, so even if you are using the H.264H.264 is a video compression standard also referred to Advanced Video Coding (AVC) or MPEG-4 Part 10 and camera then 128MB will probably be enough. On earlier models without the 3D MMU, you may need up to 256MB or 512MB in some more unusual cases.
Memory
RAM
The RPi4B LPDDRLow-Power Double Data Rate4 SDRAMSynchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory from Micron Technology is a low power equivalent to the DDRDouble Data Rate (DDR) is a type of SDRAM memory that fetches data on both the leading edge and the falling edge of the clock signal that regulates it.4 memory used in most modern higher end computers. The LPDDRLow-Power Double Data Rate4 allows for greater memory sizes, currently available up to 8GB and may increase in the future. Benchmarks from MagPi and Tom's Hardware show read/write data transfer speed around 4GB/s to 5GB/s. Compared to earlier versions of the RPi, the higher bandwidth provides more processing power for use in computationally intensive operations like Computer Vision. The figure below shows the location of the RAMRandom Access Memory chip next to the SoC on the RPi4B.
The RPi4B currently comes with 3 different versions of RAMRandom Access Memory (2GB, 4GB, and 8GB), with an increasing price tag (more memory cost more money). The 1GB model was originally available at launch in June 2019 but was discontinued in March 2020.
The RAMRandom Access Memory chip has unique identification numbers for each memory size (2GB, 4GB, and 8GB). The first 5-digit code is the part number and the second 5-digit code is the FBGAFine Ball Grid Array code. For example, in the figure above the part number is 9FD77 and the FBGAFine Ball Grid Array code is D9WHV, which means it's a 4GB chip. The FBGAFine Ball Grid Array code can be entered into an online tool at the Micron website to obtain the full part number. The following table lists the Part, FBGAFine Ball Grid Array, and full part number for each RAM size chip.
| Size | Part | FBGA | Part Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2GB | 9LD77 | D9WHZ | MT53D512M32D2DS-053 WT:D |
| 4GB | 9FD77 | D9WHV | MT53D1024M32D4DT-053 WT:D |
| 8GB | OAA47 | D9ZCL | MT53E2G32D4NQ-046 WT:A |
The meaning of each term in the full part number is provided in the figure below from the 2GB and 4GB LPDDRLow-Power Double Data Rate4 SDRAMSynchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory datasheet.
microSD
The RPi4B uses a microSDThe microSD is a Secure Digital (SD) removable miniaturized flash memory card that is the compact version of a standard SD card and is meant to be used with smaller devices. format flash card as its primary non-volatile storage for the operating system and program memory. Applying power to the RPi causes a bit of computer code stored on the board (the bootloader) to check for the presence of the microSD card in its slot and look for code on the card telling it how to start and what to load into RAMRandom Access Memory. If no card is present or a card is blank/corrupted, the RPi simply does not start.
The microSDThe microSD is a Secure Digital (SD) removable miniaturized flash memory card that is the compact version of a standard SD card and is meant to be used with smaller devices. port is on the backside edge of the RPi, as shown in the figure below. The SDSecure Digital removable miniaturized flash memory cards socket supports 1.8V, DDRDouble Data Rate (DDR) is a type of SDRAM memory that fetches data on both the leading edge and the falling edge of the clock signal that regulates it.50 mode (at a peak bandwidth of 50MB/s). A legacy SDIOSecure Digital Input Output (SDIO) is a communication interface that allows devices to connect to an SD card and exchange data. interface is also available on the GPIOGeneral Purpose Input Output pins.
The RPi4B has an 8GB minimum SDSecure Digital removable miniaturized flash memory cards card requirement (the Raspbian OSOperating System is around 5GB) stated in the RPi Getting Started Documentation SD Card Section. For most RPi projects, a 32GB SD card is enough memory, but you you can go as high as you want (SD cards that have a 64GB capacity and up require exFAT file system formatting).
A class 10 A1 rated SD card is typically recommended. A general-purpose OSOperating System, like Raspbian, tends to perform frequent smaller non-sequential I/OInput/Output read and writes on non-contiguous areas of the card, which means that "random" IOPSInput/Output operations Per Second performance becomes the dominant factor for speed. So you want to look for a card that has fast random speeds. However, these speeds are usually not related to a card's class, but rather on a card to card basis on how they perform.
One other consideration for card speed is that little else matters beyond the DDRDouble Data Rate (DDR) is a type of SDRAM memory that fetches data on both the leading edge and the falling edge of the clock signal that regulates it.50 transfer mode which supports a max bandwidth of 50MB/s (see RPi4B Datasheet PDF). For even higher IOPSInput/Output operations Per Second a USBUniversal Serial Bus 3.0 SSDSolid State Drive would be the best performer. There is only one PCIePeripheral Component Interconnect Express lane, and that lane is dedicated to the USBUniversal Serial Bus hub.
USB
The RPi4B has two Type-A USBUniversal Serial Bus 2.0 ports and two Type-A USB 3.0 ports shown in the figure below. The USB controller VL805 chip by VLIVIA Labs Inc is connected over a single PCIePeripheral Component Interconnect Express Gen 2 lane, providing a total of 4GbpsGigabits per second of bandwidth shared between the four USB ports.
The VL805-Q6 Product Page has some more details about this chip. There does not seem to be an official source of the datasheet, but someone on this NVIDIA forum uploaded the datasheet.
Ethernet
The RPi4B has a Gigabit RJ45RJ45 is the most common type of the connector used for Ethernet networking. RJ stands for “Registered Jack” and 45 refers to the interface standard number. It has eight pins, which means that it contains eight separate wires. Ethernet Port with its own Broadcom BCM54213PE controller ICIntegrated Circuit.
The Ethernet of the RPi4B has more throughput compared to the previous RPi3 due to separate USB and Ethernet controller ICIntegrated Circuits rather than being funneled via a single USB chip. The Gigabit Ethernet Broadcom BCM54213PE controller shown in the figure below is a triple-speed 1000BASE-T/100BASE-TX/10BASE-T Gigabit Ethernet (GbEGigabit Ethernet (GbE) provides a data rate of 1 billion bits per second.) transceiver integrated into a single monolithic CMOSComplementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor chip.
This chip includes digital adaptive equalizers, ADCAnalog-to-Digital Converter (ADC, A/D, or A-to-D)s, PLLPhase-Locked Loops, line drivers, encoders, decoders, echo cancellers, crosstalk cancellers, and all required support circuitry. The link between the CPU and Gigabit Ethernet is over a Reduced Gigabit Media-Independent Interface (RMGIIReduced Gigabit Media Independent Interface) Link (see Wikipedia RMGII). With most serial interfaces, there are two main parts: a Media Access Controller (MACMedium Access Control, Medium Access Controller, Media Access Control, or Medium Access Controller) and a physical interface (PHY). The idea behind this design is that the physical connection between two devices can change just by changing the PHY. There are standard buses to connect between a MAC and PHY which make interchangeability possible.
In order to be reliable over a worst-case category 5 cable or slower network speeds, the BCM54213PE automatically negotiates with its link partner to determine the highest possible operating speed. This allows the network to dictate the data transfer speed where the chip can revert to slower speeds if the network is not delivering fast enough. The device also detects and corrects most common wiring problems and features CableChecker™ diagnostics, which detects common cable problems including shorts, opens, and cable length.
There does not seem to be an official source of the BCM54213PE datasheet, but more details about this chip can be found on Broadcom's BCM54213PE Product Page.
Wireless Communication
The RPi4B has WiFi 802.11IEEE 802.11 is a set of protocol standards that define communication for a Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN). In order for WiFi to work between different devices, they all need to agree on how they are going to communicate. The current version of the standard is IEEE 802.11-2007, with many amendments such as 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, and 802.11n.ac dual-band (2.4GHz and 5GHz) wireless LANLocal Area Network and Bluetooth 5.0 at 2.4GHz. WiFi and Bluetooth are integrated into the Cypress CYW43455 (aka BCM43455) ICIntegrated Circuit chip shown in the figure below (the Cypress chip is hidden underneath the metal RF shield).
The original chip development was done by Broadcom, who named the chip BCM43455 when they released it. Broadcom later sold their Wireless IoTInternet Of Things division to Cypress who named it CYW43455. More details about the CYW43455 can be found on the CYW43455 Product Page and in the CYW43455 Datasheet (PDF).
The WiFi and Bluetooth antenna is located between the CYW43455 and the edge of the board. The design of the antenna comes from a Swedish company called Proant. They've created a triangular shape resonance cavity on the PCBPrinted Circuit Board made by removing several layers of copper. It works by having a triangular cavity in the board's ground plane, within which radio waves can resonate and focus down to the narrow end of the cavity, where they are received or transmitted.
WiFi
The CYW43455 supports 20MHz, 40MHz, and 80MHz channel widths. The WiFi data transfer speeds depends on the connection and bandwidth chosen. Benchmark tests were performed by MagPi that measured about 58.3Mbps at 2.4GHz and 114Mbps at 5GHz. The transfer speed will ultimately be limited by the RPi4B hardware which supports a single data stream with MSC7, so the data rates will be capped at 72Mbps with a 20MHz channel, 150Mbps with a 40MHz channel, and 325Mbps on a 80MHz channel.
The CYW43455 cannot run WiFi simultaneously on dual band (2.4GHz and 5GHz), also known as Real Simultaneous Dual Band (RSDBReal Simultaneous Dual Band). However, you could add a USBUniversal Serial Bus WiFi module, to have two devices, each on a different band. There are very few production WiFi chips that supports concurrent dual band operation. This is because there will be signal interference problems from the TXTransmit/RXReceive radio circuits being so close to each other on a single chip. There are also thermal issues to deal with due to the dual band power amplifier working concurrently.
Bluetooth
The RPi4B supports Bluetooth 5.0 and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLEBluetooth Low Energy) connectivity at 2.4GHz with transfer speeds up to 2MbpsMegabits per second. The difference between the Bluetooth 5.0 and BLEBluetooth Low Energy is its application. Bluetooth 5.0 is commonly used in devices that require long term continuous exchange of data, like earphones, video game controllers, speakers, and keyboards. BLEBluetooth Low Energy is a Bluetooth standard that works with Bluetooth enabled devices and is useful for low battery consumption when data exchange is minimal, like sensor data monitoring, control of devices, etc.
The Bluetooth 5.0 support on the RPi4B is limited to only the mandatory features. The RPi4B does not support any of the Bluetooth 5.0 optional features (e.g., long range support LE Coded PHYLow Energy Coded PHY is a long-range PHY introduced in Bluetooth 5.0. , 2M PHY2 Megabit PHY (2M PHY) is a PHY configuration introduced in Bluetooth 5.0 to increase the symbol rate at the PHY layer., etc.) due to limited space and the need for extra hardware support.
Display Ports
HDMIHigh-Definition Multimedia Interface and DSIDisplay Serial Interface and are the two main methods of connecting a display to the RPi4B and there are a several factors to consider when choosing between them.
- Transfer Speed:
- DSI and HDMI are both high speed.
- Audio:
- HDMI has audio support for the screen, but DSI does not.
- Power:
- DSI has the ability power the display from the RPi, whereas HDMI cannot. DSI also has less power consumption than HDMI and better suited for battery power or when you want to minimize the load on your power supply. HDMI has a more generic protocol than DSI, which needs to be converted to something a specific LCD controller understands, so you have to power an additional HDMI to DSI converter.
- Screen Size:
- HDMI can scale to much larger screens, while the DSI is meant for smaller LCDs. HDMI has a wide range of available screens, but small HDMI screens are expensive. DSI only supports a single screen compared to the RPi dual screen option with HDMI.
- Mounting:
- If you're trying to attach the screen to the RPi board in a more compact form, the position of DSI port at the end of the board with the flexible DSI ribbon cable cable makes this a better option than the HDMI plug and cord.
- Interchangeability:
- Unlike HDMI, DSI displays are designed for specific devices, and are commonly used for flat panel displays of tablets and smartphones. DSI LCDs that connect to the RPi are specifically designed for the RPi and usually you will not be able to use it on any other device. This is because the display driver for the LCD is programmed to work with the GPU in the RPi SoC.
HDMI
The RPi comes with two Micro HDMIHigh-Definition Multimedia Interface connectors that carries sound and images from your RPi to one or dual display computer monitors, HDHigh Definition TV, or projector. The HDMI ports provide a high-speed digital transfer with 4K4K resolution refers to a horizontal display resolution of approximately 4,000 pixels. In television and consumer media, 3840 x 2160 (4K UHD) is the dominant 4K standard. resolution on one screen at 60fpsFrames Per Second or 4K4K resolution refers to a horizontal display resolution of approximately 4,000 pixels. In television and consumer media, 3840 x 2160 (4K UHD) is the dominant 4K standard. resolution at 30fpsFrames Per Second on two screens.
There are different versions of HDMI with a few listed below to see the differences (a more complete list can be found on Wikipedia HDMI). The RPi3 has support for HDMI 1.3 whereas the RPi4B has support for HDMI 2.0.
| Version | Transmission Bandwidth |
Resolution | HDRHigh Dynamic Range | HDCPHigh-bandwidth Digital Content Protection (HDCP) is a form of digital copy protection to prevent copying of digital audio and video content as it travels across connections. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDMI 1.3 | 10.2GbpsGigabits per second | 1080p601920 x 1080 progressively displayed pixels; also known as Full HD or FHD, and BT.709. 1,920 pixels are displayed across the screen horizontally and 1,080 pixels down the screen vertically. The p stands for progressive scan, i.e. non-interlaced. The 60 stands for 60 frames per second. | No | 1.2 |
| HDMI 1.4 | 10.2GbpsGigabits per second | 4Kp304K resolution refers to a horizontal display resolution of approximately 4,000 pixels. In television and consumer media, 3840 x 2160 (4K UHD) is the dominant 4K standard. The p stands for progressive scan, i.e. non-interlaced. The 30 stands for 30 frames per second. | No | 1.4 |
| HDMI 2.0 | 18.0GbpsGigabits per second | 4Kp604K resolution refers to a horizontal display resolution of approximately 4,000 pixels. In television and consumer media, 3840 x 2160 (4K UHD) is the dominant 4K standard. The p stands for progressive scan, i.e. non-interlaced. The 60 stands for 60 frames per second. | Yes | 2.2 |
DSI
At the top edge of the RPi board, next to the label DISPLAY on the PCBPrinted Circuit Board, is a Display Serial Interface (DSIDisplay Serial Interface) connector (a small 15-pin ribbon connector protected by a layer of plastic) used for a touchscreen display or other LCDLiquid Crystal Display display specifically designed for the RPi. In order to connect an LCD to the DSI port on a RPi, you need a DSI compatible display for the RPi with a 15-pin ribbon cable and a display driver for the GPU in the SoC.
DSI is a high-speed serial interface between the host processor (RPi) and a display module. The interface inside the SoC is specified by the Mobile Industry Processor Interface (MIPIMobile Industry Processor Interface), defining the serial bus and communication protocol between the host, source of the display data, and the destination device.
Using the MIPI interface, the SoC feeds graphics data directly to the display panel through the DSI connector. The DSI connector pinout shown below is from the RPi4B Schematics, followed by a table describing each of the pin functions.
| Pin # | Function |
|---|---|
| 1 | Ground |
| 2 | DSI1_DN1 Data Lane 1 Negative |
| 3 | DSI1_DP1 Data Lane 1 Positive |
| 4 | Ground |
| 5 | DSI1_CN Clock Negative |
| 6 | DSI1_CP Clock Positive |
| 7 | Ground |
| 8 | DSI1_DN0 Data Lane 0 Negative |
| 9 | DSI1_DP0 Data Lane 0 Positive |
| 10 | Ground |
| 11 | SCL0 I2C Serial Clock Line |
| 12 | SDA0 I2C Serial Data Line |
| 13 | Ground |
| 14 | +3.3V |
| 15 | +3.3V Power Supply |
The DSI specifies a serial bus with one high speed clock lane (DSI1_CN/DSI1CP) and two data lanes used in parallel to transmit data (Lane 0 is DSI1_DN0 and DSI1_DP0, whereas Lane 1 is DSI1_DN1 and DSI1_DP1).
Each lane is carried on two wires for differential signaling with a low voltage around 200mV, known as Low Voltage Differential Signaling (LVDSLow Voltage Differential Signaling). A differential signaling system transmits information as the difference between the voltages on a pair of wires, where the two wires are compared at the receiver to determine the logic level. LVDSLow Voltage Differential Signaling has the advantage of operating at low power and can run at high speeds using inexpensive twisted-pair copper cables.
The I2CInter-Integrated Circuit. Also referred to as IIC or I2C. serial clock (SCL0) and data (SDA0) lines on pins 11 and 12 are used to configure the DSI interface on some displays. The original RPi1 didn't have any I2C on the DSI header, requiring users to manually wire the I2C for the touchscreen.
Audio-Video
CSI
On the edge of the RPi board next to the label CAMERA on the PCBPrinted Circuit Board, shown in the figure below, is a 15-pin Camera Serial Interface (CSICamera Serial Interface) connector with a plastic flap that can be pulled up. This port provides a high speed connection with a specifically designed RPi camera module that can record still images and video.
There is no audio over the CSI, but you can connect a separate line from a camera module with an audio I2SInter-IC Sound output, or connect a camera to an HDMI to CSI bridge, to the RPi4B GPIO I2S input. You can also use a separate microphone sensor for audio.
You can use a USBUniversal Serial Bus camera with the RPi, but the board has a limited number of USB ports that may be used for a keyboard, mouse, or other peripherals. Camera modules that connect to the CSI port also draw less power than USB webcams, so it doesn't strain the power supply or drain the batteries.
The RPi CSI camera connects to a Zero Insertion Force (ZIF) 15 socket with a 15-pin ribbon flex cable that transfers data over a CSI-2 bus to the SoC. The CSI-2 specification offers up to four data lanes on the bus, but the RPi uses only uses two data lanes because the GPU VideoCore multimedia processor does not have enough processing power to take advantage of the 4-lane bandwidth.
CSI is a high-speed serial interface between the host processor (RPi) and a camera module. The interface inside the SoC is specified by the Mobile Industry Processor Interface (MIPI), defining the serial bus and communication protocol between the host and camera device. Using the MIPI interface, the camera image sensor transfers image data through the CSI cable and connector to the SoC over the serial bus. The CSI connector pinout shown below is from the RPi4B Schematics, followed by a table describing each of the pin functions.
| Pin # | Function |
|---|---|
| 1 | Ground |
| 2 | CAM1_DN1 Data Lane 1 Negative |
| 3 | CAM1_DP1 Data Lane 1 Positive |
| 4 | Ground |
| 5 | CAM1_CN Clock Negative |
| 6 | CAM1_CP Clock Positive |
| 7 | Ground |
| 8 | CAM1_DN0 Data Lane 0 Negative |
| 9 | CAM1_DP0 Data Lane 0 Positive |
| 10 | Ground |
| 11 | CAM_GPIO Power Enable |
| 12 | No Connection |
| 13 | SCL0 I2C Serial Clock Line |
| 14 | SDA0 I2C Serial Data Line |
| 15 | +3.3V Power Supply |
The CSI specifies a serial bus with one high speed clock lane (CAM1_CN/CAM1CP) and two data lanes used in parallel to transmit data (Lane 0 is CAM1_DN0 and CAM1_DP0 and Lane 1 is CAM_DN1 and CAM1_DP1). Each lane is carried on two wires for differential signaling with a low voltage, known as Low Voltage Differential Signaling (LVDSLow Voltage Differential Signaling).
The I2CInter-Integrated Circuit. Also referred to as IIC or I2C. serial clock (SCL0) and data (SDA0) lines on pins 11 and 12 are used to configure/control camera functions like selecting the image resolution, frame rate, etc. The original RPi1 didn't have any I2C on the DSI header, requiring users to manually wire the I2C for the touchscreen.
CAM_GPIO is used to drive the camera, and power it up/down, when it is required.
Audio-Video Output
The Pi4B supports near-CD-quality analog audio output (2-channel stereo) and standard RCARadio Corporation of America composite TV output via a 3.5mm 4-ring TRRSTip-Ring-Ring-Sleeve (TRRS) audio connector AVAudio Video jack. The analog audio output can drive 32 Ohm headphones directly.
GPIO
The RPi4B General Purpose Input Output (GPIOGeneral Purpose Input Output) header has 40 pins that can be used to send data in and out of the RPi4B along with a few power pins.
The GPIO header consists of the following options:
- 2x 5V DC input/output power pins
- 2x 3.3V DC output power pins
- 8x GND pins
- 26x Digital I/O
- 4x PWM
- 1x UART
- 1x I2C
- 1x SPI
- 1x PCM (I2S)
- 1x I2C EEPROM
There are no analog inputs on the RPi4B, since there is no onboard ADCAnalog-to-Digital Converter (ADC, A/D, or A-to-D), but you can connect an external ADC module that communicates with the board by I2CInter-Integrated Circuit. Also referred to as IIC or I2C. or SPISerial Peripheral Interface. All digital I/OInput/Output data pins are 3.3V, so interfacing with external 5V devices requires a voltage level shift (a direct connection a GPIO pin to a voltage higher than 3.3V will likely destroy the GPIO block within the SoCSystem On a Chip).
There are several different numbering schemes for the pins, but the two most common are the physical pin numbers (1 to 40) and the Broadcom BCMBroadcom numbers (GPIO0 to GPIO26). Which numbering scheme to use is up to you, but you need to designate the one you plan on using at the beginning of your software program (e.g., in the RPi.GPIO library the command GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD) designates the physical pin numbers and GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) is for using the Broadcom pin numbers).
Some pins have special features, such as PWMPulse-Width Modulation, UARTUniversal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter, I2CInter-Integrated Circuit. Also referred to as IIC or I2C., SPISerial Peripheral Interface, and PCMPulse-Code Modulation (I2SInter-IC Sound). Each of these are described briefly below.
- PWMPulse-Width Modulation:
-
Pulse-Width Modulation (PWMPulse-Width Modulation) can be used to control the brightness of an LED, control motors,
and can provide limited analog-like output.
- Pins are 3.3V when turned HIGH and 0V when turned LOW with the output signal pulsating between states
- Software PWM available on all GPIO pins (only suitable for low frequency signals)
- Hardware PWM available on GPIO 12, GPIO 13, GPIO 18, and GPIO 19
- UARTUniversal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter:
-
UARTUniversal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter is an asynchronous (no clock data transmitted in order to synchronize transmission) serial
data protocol sed to transfer serial data, one bit at a time, between devices
- Only two signal lines: telephone line, the transmit data connection (TXDTransmit Data) from one end is connected to the receive data connection (RXDReceive Data) on the other end of the connection, and vice versa
- TX (GPIO14); RX (GPIO15)
- I2CInter-Integrated Circuit. Also referred to as IIC or I2C.:
-
I2CInter-Integrated Circuit. Also referred to as IIC or I2C. is an asynchronous (no clock data transmitted) serial data protocol intended to allow
multiple "slave" digital integrated circuits to communicate with one or more "master"
- Intended for short communication distances
- Only requires two signal wires to exchange information
- Data: (GPIO2); Clock (GPIO3)
- I2CInter-Integrated Circuit. Also referred to as IIC or I2C. EEPROMElectrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory:
- ID_SD and ID_SC pins (EEPROM Data GPIO0, EEPROM Clock GPIO1) are reserved for HAT ID EEPROM. At boot time this I2C interface will be interrogated to look for an EEPROM that identifies the attached board and allows automatic setup of the GPIOs. Do not use these pins for anything other than attaching the I2C ID EEPROM. Leave unconnected if ID EEPROM is not required.
- SPISerial Peripheral Interface:
-
SPISerial Peripheral Interface is synchronous serial data protocol used for communication between multiple peripheral
devices (e.g., shift registers, sensors, and SDSecure Digital removable miniaturized flash memory cards cards in the Pi) or microcontrollers
quickly over short distances. SPI can utilize different clock and data lines (MISOMaster In Slave Out (MISO) is the SPI data output line from the slave device,
MOSIMaster Out Slave In (MOSI) is the SPI data output line from the master device, SCKSerial Clock line), along with a select line (SSSlave Select (SS) is the SPI output line from the master device to indicate that data is being sent. Also referred to as Chip Select (CS).), to choose to
communicate with which device.
- SPI0: MOSI (GPIO10); MISO (GPIO9); SCLK (GPIO11); CE0 (GPIO8), CE1 (GPIO7)
- SPI1: MOSI (GPIO20); MISO (GPIO19); SCLK (GPIO21); CE0 (GPIO18); CE1 (GPIO17); CE2 (GPIO16)
- PCMPulse-Code Modulation (I2SInter-IC Sound):
-
The RPi4B comes with Pulse-Code Modulation (PCMPulse-Code Modulation) pins for digital
audio from an I2SInter-IC Sound audio device. PCM is a digital representation of an analog audio signal and
I2S is an electrical serial interface used to transmit PCM data from one device to another.
- Din: GPIO 20 input data from an I2S audio device, such as a microphone.
- Dout: GPIO 21 provides a data output signal to an external audio device such as a DACDigital-to-Analog Converter (DAC, D/A, or D-to-A) chip.
- FS: GPIO 19 provides a frame-sync signal to an external audio device such as a DACDigital-to-Analog Converter (DAC, D/A, or D-to-A) chip.
- CLK: GPIO 18 provides a clock signal to an external audio device such as a DACDigital-to-Analog Converter (DAC, D/A, or D-to-A) chip.
Power
There are three inputs that can be used to power the RP4B:
- 5V 3A DC via USB-C connector
- Regulated 5V 3A DC via GPIO header
- Power over Ethernet (PoE)
The RPi4B does not have a power switch. The typical way to turn on the RPi4B on is to just plug it in. To turn it off, you shut down the OSOperating System and then unplug the power cable. There are power switches available that you can buy to switch the power on/off, but always shut down the OS before cutting the electricity.
USB-C
The Pi4B requires a good quality USB-C power supply capable of delivering 5V at 3A. A 5V 2.5A supply may be used if USB devices attached downstream consume less than 500mA. You can also power the RPi4B off of a USB PDUSB Power Delivery (USB PD) is a specification that enables the maximum functionality of USB by providing more flexible power delivery along with data over a single cable. It operates by facilitating a conversation between two devices to negotiate a power contract so they can determine how much power can be pulled from the charger. power bank that you would use to charge a phone. The USB-C power circuitry on the RPi4B board uses the MaxLinear MxL7704 Power Management IC (PMICPower Management Integrated Circuit (PMIC)). Details on MxL7704 IC can be found in the MxL7704 Datasheet (PDF).
GPIO
Another way to power up the RPi4B is by apply a well regulated 5V 2.5A supply to GPIO pins 2 and 4 and connecting ground to any of the GNDCommon Ground pins (6, 9, 14, 20, 25, 30, 34 or 35). This can be accomplished either using a battery or a power adapter. It is advisable to apply 5V to both pins 2 and 4, so that if one pin is unable to provide an accurate 5V the other pin can compensate for that. However, make sure that you do not connect both a USB-C power supply and power through the GPIO.
PoE
There are 4-pins in a square formation just behind the Ethernet connector that can be used to power the RPi4B with the RPi PoE HAT or RPi PoE+ HAT accessory.
The Raspberry Pi PoE/PoE+ HATs power the RPi4 board via an Ethernet cable, where power-sourcing equipment is required on the Ethernet network. The RPi4B PoE pins connect to the unused connections in the Ethernet jack and voltage supplied over these pins are passed through a voltage regulator and then fed into the RPi4B.
Conclusion
This hardware overview of the RPi4B covered specs, board layout, pinout, processors, memory, I/O, and power. The RPi4B can be used in applications where space is limited, lower power consumption is needed, and/or lower cost is desired, compared to a full-sized desktop or laptop computer. The GPIO pins can directly interface to I/O components such as switches, sensors, ADCAnalog-to-Digital Converter (ADC, A/D, or A-to-D)s, LCDLiquid Crystal Display/OLEDOrganic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) displays, Relays, RTCReal-Time Clocks, Timers, and many more devices.
The RPi4B has very good performance, is very reliable, with a lot of documentation available, making it one of the best values you can get from an SBC.
References
| Category | Reference Description | Links |
|---|---|---|
| Board | raspberrypi.com Raspberry Pi 4 Webpage includes links to Documentation, Getting Started Guides, and Software Images | raspberrypi.com |
| Raspberry Pi 4B Datasheet (PDF) | RPi4B Datasheet PDF | |
| Raspberry Pi 4B Schematics (PDF) | RPi4B Schematics | |
| Raspberry Pi 4B Mechanical Drawing (PDF) | RPi4B Mechanical Drawing | |
| SoC | BCM2711 ARM Peripherals Datasheet (PDF) | BCM2711 Datasheet |
| CPU | Wikipedia ARM Cortex-A72 CPU of the RPi4B | Wikipedia ARM Cortex-A72 |
| GPU | Wikipedia VideoCore GPU of the RPi4B | Wikipedia VideoCore |
| Memory | MagPi Read/Write data transfer speed benchmarks | MagPi |
| Tom's Hardware Read/Write data transfer speed benchmarks | Tom's Hardware | |
| RAM identification numbers online tool | Online Tool | |
| USB | The USB controller VL805 chip Product Page | VL805-Q6 Product Page |
| Ethernet | Wikipedia Reduced Gigabit Media-Independent Interface (RMGII) | Wikipedia RMGII |
| Broadcom's Gigabit Ethernet BCM54213PE Controller Product Page | BCM54213PE Product Page | |
| WiFi/BT | Cypress CYW43455 Chip Product Page | CYW43455 Product Page |
| Cypress CYW43455 Chip Datasheet (PDF) | CYW43455 Datasheet | |
| HDMI | Wikipedia HDMI versions | Wikipedia HDMI |
| Power | MaxLinear MxL7704 Power Management IC (PMIC) Datasheet (PDF) | MxL7704 Datasheet |
| Product page for RPi PoE HAT | RPi PoE HAT | |
| Product page for RPi PoE+ HAT | RPi PoE+ HAT |
Products
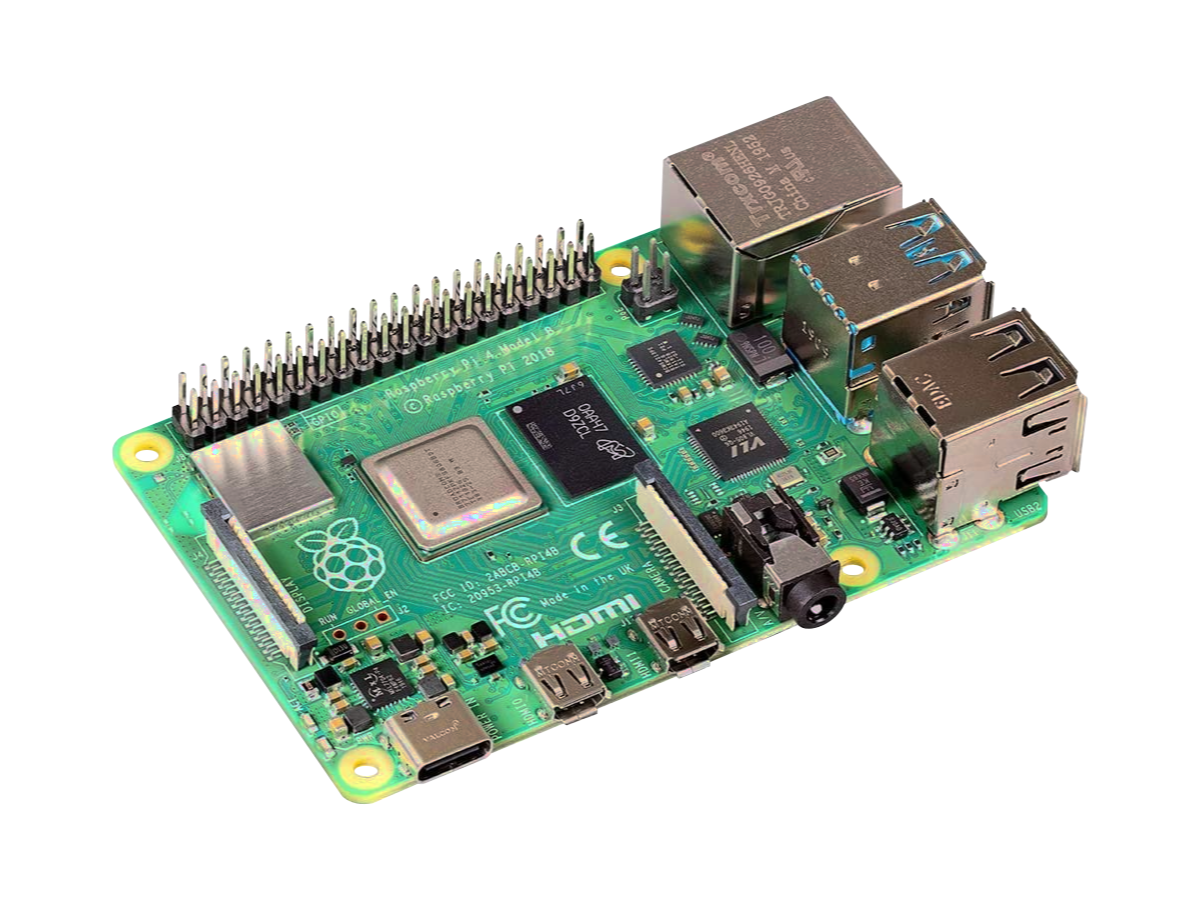
Created:
06Mar2023 18:39:17 UTC
2023-03-06T18:39:17Z
Updated:
03Sep2024 07:40:55 UTC
2024-09-03T07:40:55Z
- Processors:
-
- Broadcom BCM2711 SoCSystem On a Chip with Quad-Core Cortex-A72 (ARM v8) 64-bit @ 1.5GHz CPUCentral Processing Unit and VideoCore VI GPUGraphics Processing Unit
- Memory:
-
- 1GB, 2GB, 4GB or 8GB LPDDRLow-Power Double Data Rate4-3200 SDRAMSynchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (depending on model)
- microSDThe microSD is a Secure Digital (SD) removable miniaturized flash memory card that is the compact version of a standard SD card and is meant to be used with smaller devices. card slot for loading operating system and data storage
- Connectivity:
-
- 2.4GHz and 5.0GHz IEEEInstitute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (Industry Standards) 802.11IEEE 802.11 is a set of protocol standards that define communication for a Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN). In order for WiFi to work between different devices, they all need to agree on how they are going to communicate. The current version of the standard is IEEE 802.11-2007, with many amendments such as 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, and 802.11n.ac wireless, Bluetooth 5.0 (BLEBluetooth Low Energy), Gigabit Ethernet
- 2x USB 3.0 ports, 2x USB 2.0 ports, 2x micro-HDMI display ports, 1x 2-lane MIPIMobile Industry Processor Interface DSIDisplay Serial Interface display port, 1x 2-lane MIPI CSICamera Serial Interface camera port
- 4-pole stereo audio and composite video port
- 40-pin GPIOGeneral Purpose Input Output


(0) Comments
Sign in to leave a comment
Sign In