Microwave Motion Sensors
Updated: 25Aug2024 06:17:35 UTC 2024-08-25T06:17:35Z
Rating: (0 reviewsThis article has not been rated yet)
Microwave motion sensors are a type of active sensor that operates by sending out a microwave signal and determining any small differences in the reflected waves as a result of movement in the area.
This overview of Microwave motion sensors will cover the most common modules, how they operate, and their capabilities.
Operation
Microwave motion sensor modules are active sensors, where they transmit microwaves that reflects off different surfaces and return to a receiver in the sensor. The reflected signal is mixed with the transmitted signal to arrive at a frequency difference that is extracted by a low pass RC filter, amplified, and threshold detected.
Some common terms that when describing the characteristics of Microwave modules are given below.
- Operating Voltage:
- The operating voltage across VCC and GND provides power to the Microwave sensor module for the components in the circuitry. Microwave modules typically accept a range of voltages with onboard regulator IC that steps down and stabilizes the voltage for the circuit components.
- Output Voltage:
- The output signal voltage is typically an active HIGH 3.3V or 5V when motion is detected. When no motion is detected, the output is a LOW 0V.
- Working Current:
- This is the current consumption of the Microwave module when it is transmitting and receiving microwaves. The Microwave modules mentioned here are on the order of milliamps.
- Sensing Angle:
- This is the Field-Of-View (FOV) of the sensor specified in degrees. Some modules, like the RCWL-0516 have a 360° FOV, while others modules have horizontal angle of 72° and vertical angle of 36°.
- Sensitivity or Sensing Range:
- The sensitivity of Microwave modules determines the sensing range distance of how far from the sensor they can detect motion. Microwave modules typically range from 2m up to 16m (6ft up to 48ft).
- Frequency:
- This is the frequency of electromagnetic waves transmitted and received by the sensor. All microwave sensors operate within the frequency range of 0.3GHz to 40GHz, but most modules operate in the S Band (1.5GHz to 3.9GHz) or the X Band (8.2GHz to 12.5 GHz).
Modules
There are several Microwave modules available with different operating voltages, sensing ranges, frequencies, and the type of output signals when motion is detected. A comparison of the most common Microwave modules are listed in the table below.
| Model | RCWL-0516 | CQRobot SKU: CQRSENWB01 |
DFRobot SEN0192 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 4V - 28V DC | 3.3V / 5V ± 0.25V DC | 5V ± 0.25V DC |
| Output Voltage (High/Low) |
3.3V / 0V | 3.3V / 0V 5V / 0V |
5V / 0V |
| Working Current | 2.8mA (typical); 3mA (max) |
37mA (typical); 60mA (max) |
37mA (typical); 60mA (max) |
| Sensing Angle | 360° | Horizontal: 72° Vertical: 36° |
Horizontal: 72° Vertical: 36° |
| Sensing Range | 3m - 5m | 2m - 16m | 2m - 16m |
| Frequency | ~ 3.2GHz | 10.525GHz X-band | 10.525GHz X-band |
| Operating Temperature |
-20°C to +80°C | -20°C to +55°C | -20°C to +55°C |
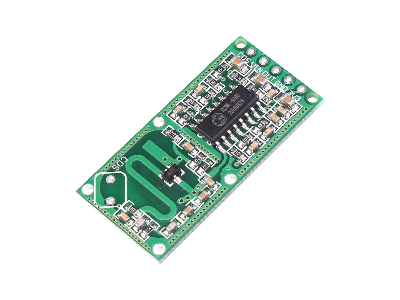
RCWL-0516
The RCWL-01516 is a 3.2GHz microwave motion sensor module has a small size of 35.9mm x 17.3mm with 360° no blind angle detection and sensing range up to 7m (21ft). It is based in the RCWL-9196 IC that processes frequency differences between the transmitted and receiving waves and outputs a high level TTL signal when motion is detected.
The main IC is the RCWL-9196 that processes the low frequency difference and has an internal 3.3V voltage regulator that allows a wide range of 4V to 28V DC for the power supply.
There are five pins with 0.1in spacing for power and the output signal. The CDS pins are an option for adding an LDRLight Dependent Resistor photoresistor to enable night only operation. LDRs are sometimes called CDS photoresistors (CDS stands for cadmium sulphide CdS, which is the photoactive component in the majority of LDRs). Each of the RCWL-0516 connections are described in the table below.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| VIN | The VIN pin is the operating supply voltage that can be from 4V to 28V DC. |
| OUT | The OUT pin is the motion detection signal output that is active 3.3V HIGH and 0V LOW |
| 3V3 | The 3.3V pin is used as an output power supply for external devices. This comes from the voltage regulator inside the RCWL-9196 IC that can supply up to 100mA. |
| CDS |
The CDS pins are an option for adding an LDR photoresistor to enable night only operation.
There are two ways to connect an LDR:
|
| C-TM | The C-TM pads are used to elongate the detection output time greater than the default of 2 seconds by the addition of a SMDSurface Mount Device capacitor. |
| R-CDS | The R-CDS pads are used to change the limit value of the photoresistor by connecting a suitable resistor (50kΩ - 100kΩ). The lower the resistor value, the brighter the light must be in order to disable the trigger. |
| R-GN | R-GN adjusts the measuring distance of the sensor by connecting a resistor. The default sensing distance is 7m, but if you connect a 1MΩ ohm resistor the detection distance is 5m. |
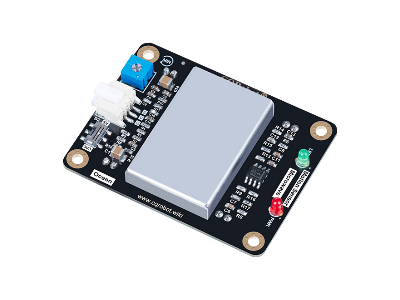
CQRobot CQRSENWB01
The CQRobot Ocean 10.525GHz Doppler Effect Microwave Motion Sensor module (SKU: CQRSENWB01) has a size of 63mm x 48mm (2.5in x 1.9in) with an adjustable sensing range from 2m to 16m and a 3dB beam-width of 72° horizontal and 36° vertical. This module usually comes with a 21cm (8.3in) cable with a 3-Pin JST broken out into three DuPont female connectors.
On the left side of the board is a 2.0PH JST connector to power the module across VCC and GND and the signal output. The module can be powered by either 3.3V or 5V using the DIP switch. This module also features trim potentiometer to adjust the sensing range between 2m and 16m.
The right side of the board has two LEDs: a red power LED indicates when the board is powered and a green signal LED that flashes when the module detects motion.
More details about this module can be found on CQRobot's product page and Wiki Page.
DFRobot SEN0192
The DFRobot Gravity Digital 10.525GHz Microwave Motion Sensor module SEN0192 has a size of 48.5mm x 63mm (1.36in x 1.05in) with an adjustable sensing range between 2m and 16m and a 3dB beam-width of 72° horizontal and 36° vertical. This module usually comes with a 3-Pin 2.0PH JST to 3-Pin female DuPont connector cable.
On the left side of the board is a 2.0PH JST connector to power the module across VCC and GND with 5V and the signal output. This module also features trim potentiometer on the bottom of the board to adjust the sensing range from 2m to 16m.
The right side of the board has two LEDs: a red power LED indicates when the board is powered and an orange signal LED that flashes when the module detects motion.
More details about this module can be found on DFRobot's product page and Wiki Page.
Conclusion
One of the benefits of microwave motion sensors is they are adaptive to environment conditions, not influenced by temperature, humidity, wind, dust, light, etc. They can also see through walls and other nonmetallic obstructions.
However, they are not without their limitations. Since they rely on reflected waves as a baseline without a moving target, they do not work well outside in open spaces. They are also prone to false-positive triggers from WiFi or cellular signals near the sensor operating frequency.






(0) Comments
Sign in to leave a comment
Sign In